Ambient Care
The project aims at the user-centered development and evaluation of a socio-technical system for context-aware provisioning and communication of professional or clinical, i.e. patient or resident-related, information.
Design essence of the AMBIENT CARE system is dynamic provisioning of different user-specific and age-based Human-Computer-Interfaces, adapted to the specific context, using in-situ generated ensembles of interaction modalities, information visualization and output devices. In contrast to existing approches using non-standard interfaces and procedures, AMBIENT CARE pursues an innovative way and realizes an open system architecture in terms of a building block system. Key principle is a strict decoupling of interaction and function.
This creates diverse marketing opportunities:
- IoT manufacturers may develop very specific devices for the nursing context. Third-party providers may develop suitable modules in an open competition.
- System vendors may develop tailored care-software-solutions for their customers using the modular architecture. The modularization of context processing and interaction eases the integration of COTS elements into new settings.
- Care facilities benefit by the flexibility of native apps or web apps in customary browsers. Hereby, specific solutions for dedicated devices and/or scaling solutions for heterogenous hardware may be realized.
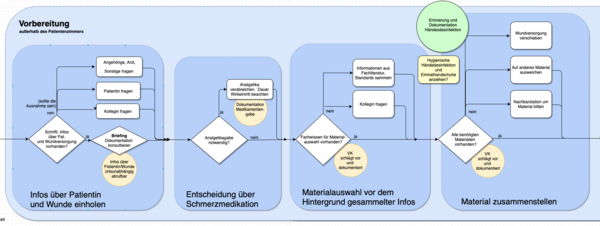
Assistance system for wound care and documentation
As a concrete application, the technical support of wound documentation and care was identified as particularly useful. Following the Human Centered Design (HCD) approach, support options for the prototypical wound care process are identified and iteratively developed in cooperation with wound care experts. Also, a "wound room" will be set up in the COPICOH HealthLab, serving as research laboratory and demonstrator. The Figure above shows a section of the wound care process in which successive assistance functions are integrated.
In order to successfully design and introduce assistance systems for caregivers as a user group, knowledge of their interaction-relevant characteristics such as interaction knowledge and experience as well as attitude towards technology is required. For this purpose, two user questionnaires were compiled on user characteristics of nurses in hospitals. The online version of the survey can be found here.
The project is carried by an interdisciplinary team of institutes at the University of Lübeck: Working Group Ambient Computing at the Institute of Telematics (ITM), Working Group age-appropriate interaction systems at the Institute for Multimedia and Interactive Systems (IMIS) and the Section for Research and Teaching in Care at the Institute of Social Medicine and Epidemiology (ISE).
Project Members
Katrin Balzer

Institut für Sozialmedizin und Epidemiologie (ISE)
+49 451 500 51262
Katrin.balzer(at)uksh.de
Nicole Jochems

Institut für Multimediale und Interaktive Systeme (IMIS)
+49 451 3101 5110
jochems(at)imis.uni-luebeck.de
Börge Kordts, M. Sc.

Institut für Telematik (ITM)
+49 451 3101 6422
kordts(at)itm.uni-luebeck.de
Swantje Seismann-Petersen

Institut für Sozialmedizin und Epidemiologie (ISE), Sektion für Forschung und Lehre in der Pflege
+49 451 500 51271
swantje.seismann-petersen(at)uksh.de
Project Manager
Andreas Schrader, Prof. Dr.-Ing.

Institut für Telematik (ITM)
+49 451 3101 6420
schrader(at)itm.uni-luebeck.de


![[Translate to english:] Link COPICOH [Translate to english:] Link COPICOH](/fileadmin/_processed_/9/1/csm_LI-In-Bug_8ed46db0dc.png)
![[Translate to english:] Link COPICOH [Translate to english:] Link COPICOH](/fileadmin/_processed_/1/b/csm_vimeo_icon_white_on_blue_rounded_b79e632cf7.png)